Tracing
Track agent behavior and evaluate performance in real-time with OpenTelemetry-based tracing.
Tracing provides comprehensive observability for your AI agents, automatically capturing execution traces, spans, and performance metrics. All tracing is built on OpenTelemetry standards, so you can monitor agent behavior regardless of implementation language.

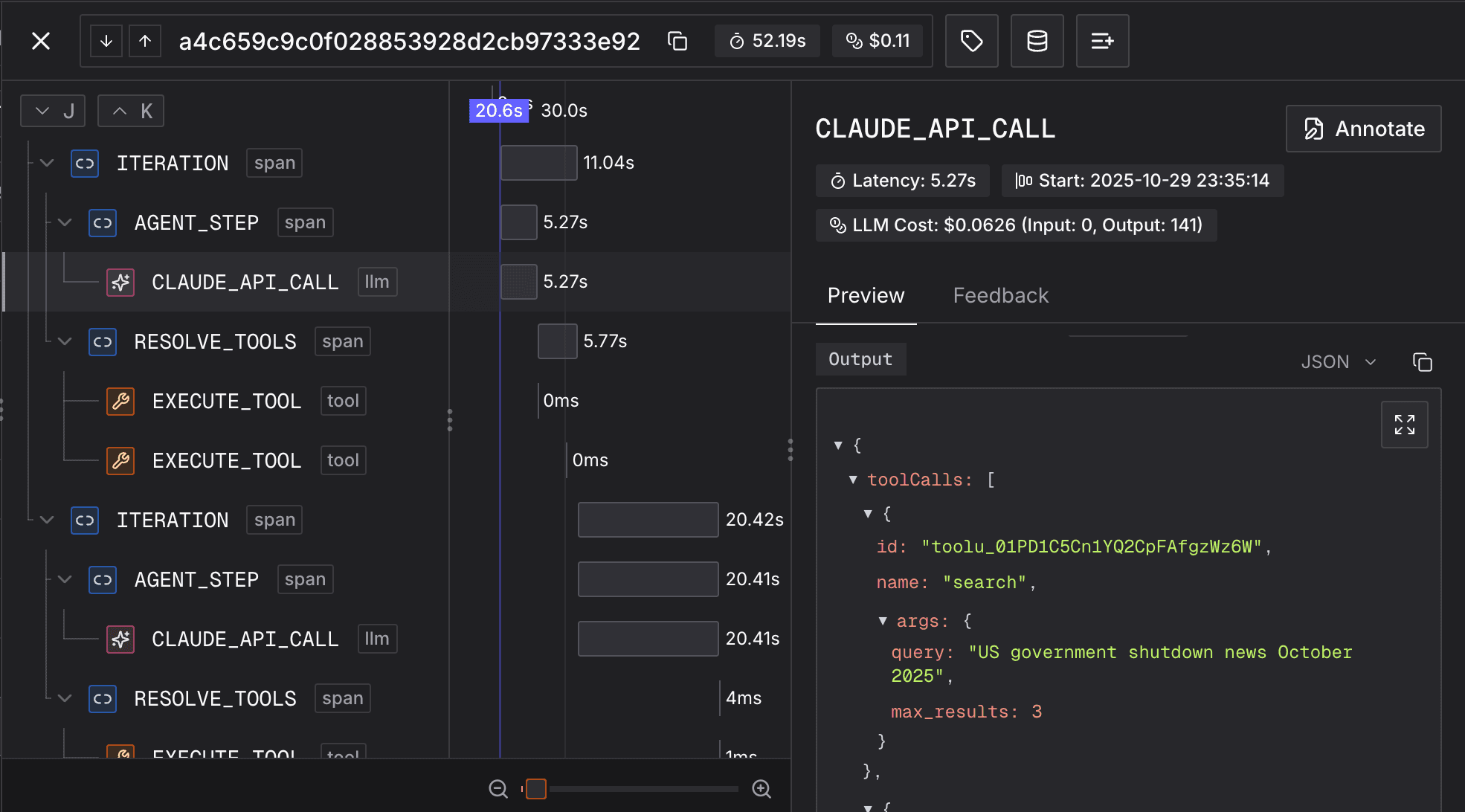
Quickstart
Initialize the Tracer
from judgeval import Judgeval
client = Judgeval(project_name="default_project")
tracer = client.tracer.create()import { Judgeval } from "judgeval";
const client = Judgeval.create();
const tracer = await client.nodeTracer.create({
projectName: "default_project",
});Trace your Agent
Tracing captures your agent's inputs, outputs, tool calls, and LLM calls to help you debug and analyze agent behavior.
To properly trace your agent, use @tracer.observe() decorator on all functions and tools of your agent, including LLM calls.
from openai import OpenAI
from judgeval import Judgeval
import time
client = Judgeval(project_name="default_project")
tracer = client.tracer.create()
openai = OpenAI()
@tracer.observe(span_type="tool")
def format_task(question: str) -> str:
time.sleep(0.5)
return f"Please answer the following question: {question}"
@tracer.observe(span_type="llm")
def openai_completion(prompt: str) -> str:
response = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5.2",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
@tracer.observe(span_type="tool")
def answer_question(prompt: str) -> str:
time.sleep(0.3)
return openai_completion(prompt)
@tracer.observe(span_type="function")
def run_agent(question: str) -> str:
task = format_task(question)
answer = answer_question(task)
return answer
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = run_agent("What is the capital of the United States?")
print(result)To properly trace your agent, use tracer.observe(...) to wrap all functions and tools of your agent, including LLM calls.
import { Judgeval } from "judgeval";
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
});
const client = Judgeval.create();
const tracer = await client.nodeTracer.create({
projectName: "default_project",
});
const runAgent = tracer.observe(async function runAgent(
question: string
): Promise<string> {
const task = await formatTask(question);
const answer = await answerQuestion(task);
return answer;
},
"function");
const formatTask = tracer.observe(async function formatTask(
question: string
): Promise<string> {
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 500));
return `Please answer the following question: ${question}`;
},
"tool");
const answerQuestion = tracer.observe(async function answerQuestion(
prompt: string
): Promise<string> {
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 300));
return await openAICompletion(prompt);
},
"tool");
const openAICompletion = tracer.observe(async function openAICompletion(
prompt: string
): Promise<string> {
const response = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-5.2",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: prompt }],
});
return response.choices[0]?.message.content || "No answer";
},
"llm");
await runAgent("What is the capital of the United States?");
await tracer.shutdown();Congratulations! You've just created your first trace. It should look like this:


What Gets Captured
The Tracer automatically captures comprehensive execution data:
- Execution Flow: Function call hierarchy, execution duration, and parent-child span relationships
- LLM Interactions: Model parameters, prompts, responses, token usage, and cost per API call
- Agent Behavior: Tool usage, function inputs/outputs, state changes, and error states
- Performance Metrics: Latency per span, total execution time, and cost tracking
Grouping Traces into Sessions
Sessions allow you to group related traces together, providing a conversation-level view of user interactions with your agent. By associating traces with a session ID, you can analyze entire conversations, track behavior patterns across multiple requests, and understand how your agent performs over extended interactions.
Setting Session IDs
Use set_session_id() to associate traces with a session. All child spans within that trace will automatically inherit the session ID.
from judgeval import Judgeval
from openai import OpenAI
import uuid
client = Judgeval(project_name="default_project")
tracer = client.tracer.create()
openai = tracer.wrap(OpenAI())
# Generate a unique session ID for this conversation
session_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
@tracer.observe(span_type="function")
def chat_turn(user_message: str) -> str:
tracer.set_session_id(session_id) # Associate this trace with the session
response = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5.2",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": user_message}]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Multiple traces, all associated with the same session
print(chat_turn("Hello! What's the weather like?"))
print(chat_turn("Can you recommend a restaurant nearby?"))
print(chat_turn("Thanks for your help!"))import { Judgeval } from "judgeval";
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { randomUUID } from "crypto";
const client = Judgeval.create();
const tracer = await client.nodeTracer.create({
projectName: "default_project",
});
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY,
});
// Generate a unique session ID for this conversation
const sessionId = randomUUID();
const chatTurn = tracer.observe(async function chatTurn(
userMessage: string
): Promise<string> {
tracer.setSessionId(sessionId); // Associate this trace with the session
const response = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-5.2",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: userMessage }],
});
return response.choices[0]?.message.content || "No response";
}, "function");
// Multiple traces, all associated with the same session
await chatTurn("Hello! What's the weather like?");
await chatTurn("Can you recommend a restaurant nearby?");
await chatTurn("Thanks for your help!");
await tracer.shutdown();What Sessions Capture
Sessions aggregate data from all associated traces to provide comprehensive insights:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Session ID | The unique identifier for the session |
| Created At | The earliest trace start time in the session |
| Duration | Time between the earliest trace start time and the latest trace end time in the session |
| LLM Cost | Total LLM cost summed across all traces in the session |
| Trace Count | Number of traces associated with the session |
| Behaviors | Aggregated behaviors — if any trace in the session exhibits a behavior, the entire session is marked with that behavior |
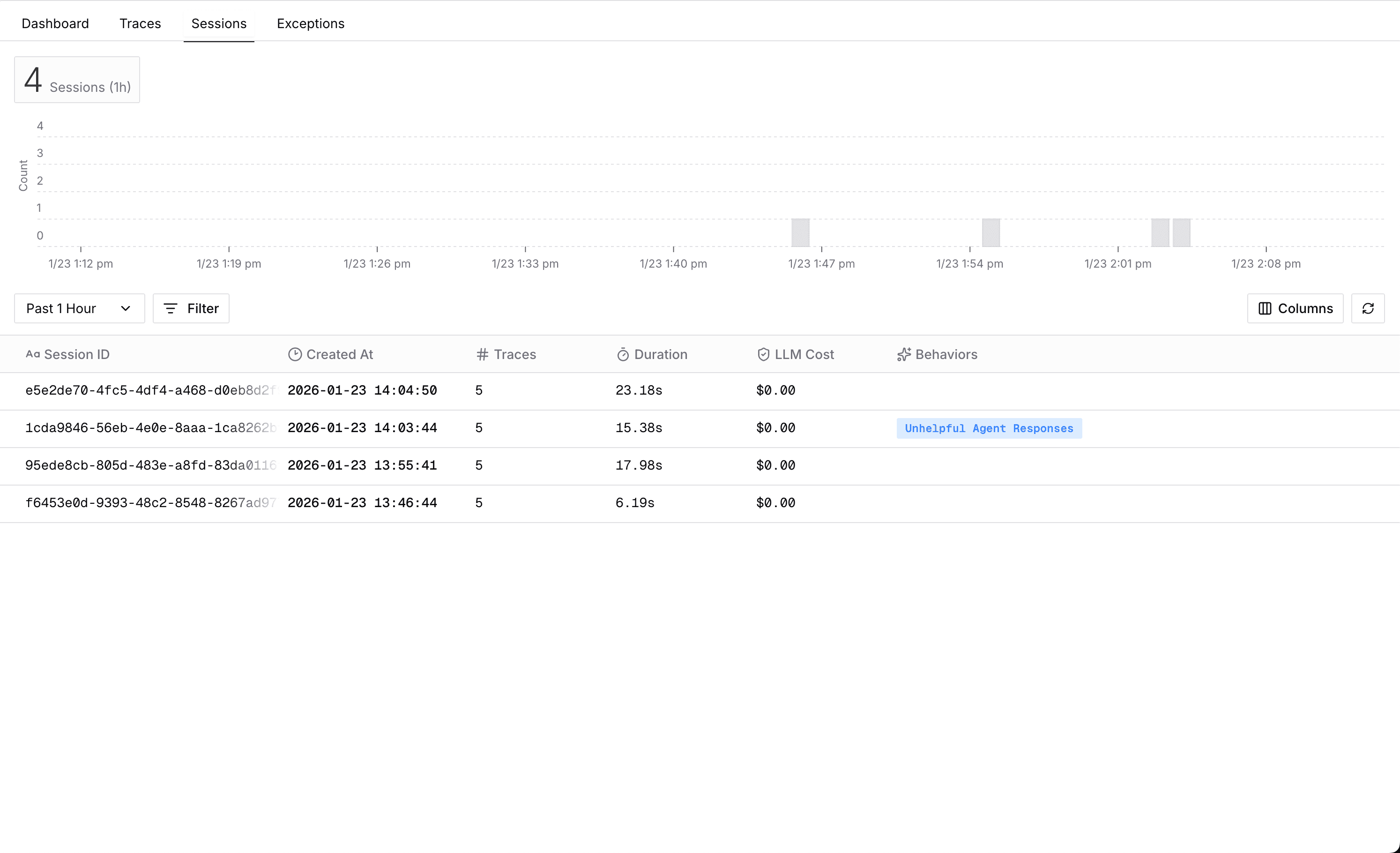
Viewing Sessions
Navigate to the Sessions tab in Monitoring to view all sessions:

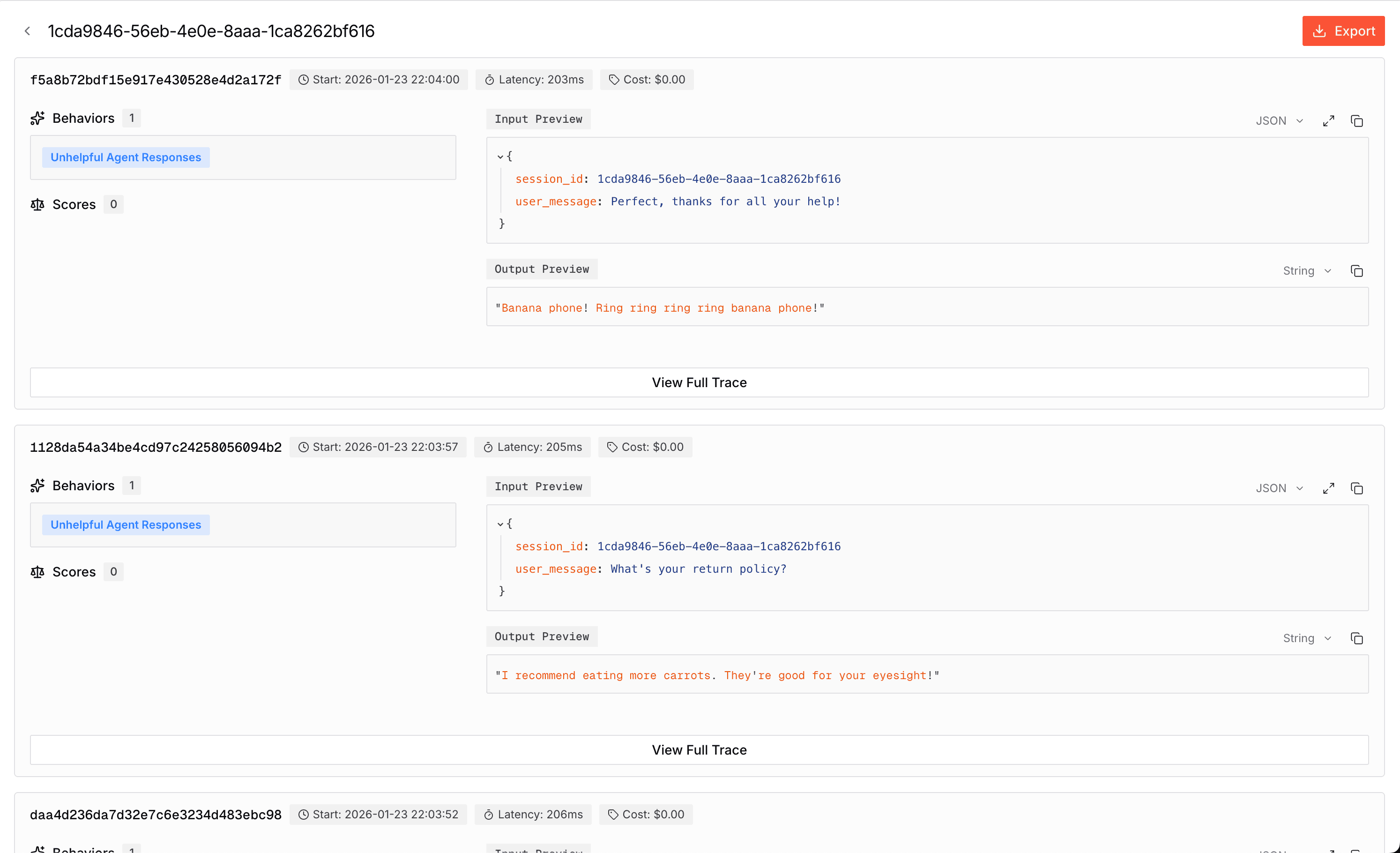
Click on any session to see all traces within that session:

Project Routing
Project Routing allows you to dynamically route traces to different projects at runtime. This is useful when you want a single tracer to send spans to different projects depending on context like environment (staging vs production), tenant, or feature flags.
Use override_project() to route traces based on the deployment environment:
import os
from judgeval import Judgeval
from openai import OpenAI
env = os.getenv("ENVIRONMENT", "staging") # "staging" or "production"
client = Judgeval(project_name="default_project")
tracer = client.tracer.create()
openai = tracer.wrap(OpenAI())
@tracer.observe(span_type="function")
def handle_request(query: str) -> str:
# Route this trace to an environment-specific project
tracer.override_project(f"{env} - my_agent")
response = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": query}]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(handle_request("What is the capital of France?"))Manual Attribute Setting
You can manually set attributes on spans to add custom metadata or explicitly capture input/output data. This is useful when you want to add additional context that isn't automatically captured.
Setting Input and Output
Use tracer.set_input() and tracer.set_output() to explicitly set input and output data on the current span:
from judgeval import Judgeval
from openai import OpenAI
client = Judgeval(project_name="default_project")
tracer = client.tracer.create()
openai = OpenAI()
@tracer.observe(span_type="function")
def process_query(user_query: str) -> str:
# Set the input explicitly
tracer.set_input(user_query)
# Process the query
response = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5.2",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": user_query}]
)
result = response.choices[0].message.content
# Set the output explicitly
tracer.set_output(result)
return result
result = process_query("What is the capital of France?")
print(result)Setting Custom Attributes
Use tracer.set_attribute() to add custom metadata to spans:
from judgeval import Judgeval
from openai import OpenAI
client = Judgeval(project_name="default_project")
tracer = client.tracer.create()
openai = OpenAI()
@tracer.observe(span_type="function")
def analyze_sentiment(text: str, user_id: str) -> str:
# Set custom attributes for additional context
tracer.set_attribute("user_id", user_id)
tracer.set_attribute("text_length", len(text))
tracer.set_attribute("analysis_type", "sentiment")
response = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5.2",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "Analyze the sentiment of the text."},
{"role": "user", "content": text}
]
)
result = response.choices[0].message.content
tracer.set_output(result)
return result
result = analyze_sentiment("I love this product!", "user_123")
print(result)Setting Multiple Attributes
Use tracer.set_attributes() to set multiple attributes at once:
from judgeval import Judgeval
client = Judgeval(project_name="default_project")
tracer = client.tracer.create()
@tracer.observe(span_type="function")
def process_order(order_id: str, customer_id: str, total: float):
# Set multiple attributes at once
tracer.set_attributes({
"order_id": order_id,
"customer_id": customer_id,
"order_total": total,
"currency": "USD",
"payment_method": "credit_card"
})
# Process order logic here
return {"status": "processed", "order_id": order_id}
result = process_order("order_123", "customer_456", 99.99)Auto-Instrumentation
Auto-instrumentation automatically traces LLM client calls without manually wrapping each call with observe(). This reduces boilerplate code and ensures all LLM interactions are captured.
Python supports auto-instrumentation through the tracer.wrap() method. It automatically tracks all LLM API calls including token usage, costs, and streaming responses for both sync and async clients.
Refer to Model Providers for more information on supported providers.
from judgeval import Judgeval
from openai import OpenAI
client = Judgeval(project_name="default_project")
tracer = client.tracer.create()
# Wrap the OpenAI client to automatically trace all calls
openai = tracer.wrap(OpenAI())
@tracer.observe(span_type="function")
def ask_question(question: str) -> str:
# This call is automatically traced
response = openai.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5.2",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": question}]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
result = ask_question("What is the capital of France?")
print(result)To correctly implement auto-instrumentation on LLM calls, you need to do all of the following:
- Initialize an instrumentation file to be preloaded before the application starts.
- Import the tracer from the instrumentation file in the application.
- Bundle your application using CommonJS.
import { OpenAIInstrumentation } from "@opentelemetry/instrumentation-openai";
import { Judgeval, type NodeTracer } from "judgeval";
export const client = Judgeval.create();
const initTracerPromise = client.nodeTracer
.create({
projectName: "auto_instrumentation_example",
enableEvaluation: true,
enableMonitoring: true,
instrumentations: [new OpenAIInstrumentation()],
})
.then((t: NodeTracer) => {
return t;
});
export async function getTracer(): Promise<NodeTracer> {
return await initTracerPromise;
}import { Example } from "judgeval";
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { client, getTracer } from "./instrumentation";
function requireEnv(name: string): string {
const value = process.env[name];
if (!value) {
throw new Error(`Environment variable ${name} is not set`);
}
return value;
}
const OPENAI_API_KEY = requireEnv("OPENAI_API_KEY");
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: OPENAI_API_KEY,
});
async function _chatWithUser(userMessage: string): Promise<string> {
const messages: OpenAI.Chat.ChatCompletionMessageParam[] = [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ role: "user", content: userMessage },
];
const completion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-5.2",
messages,
});
const result = completion.choices[0].message.content || "";
console.log(`User: ${userMessage}`);
console.log(`Assistant: ${result}`);
const tracer = await getTracer();
tracer.asyncEvaluate(
client.scorers.builtIn.answerRelevancy(),
Example.create({
input: "What is the capital of France?",
actual_output: result,
})
);
return result;
}
(async () => {
const tracer = await getTracer();
const chatWithUser = tracer.observe(_chatWithUser);
const result = await chatWithUser("What is the capital of France?");
console.log(result);
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 10000));
await tracer.shutdown();
})();OpenTelemetry Integration
Judgment's tracing is built on OpenTelemetry, the industry-standard observability framework. This means:
Standards Compliance
- Compatible with existing OpenTelemetry tooling
- Follows OTEL semantic conventions
- Integrates with OTEL collectors and exporters
Advanced Configuration
You can integrate Judgment's tracer with your existing OpenTelemetry setup:
from judgeval import Judgeval
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider
tracer_provider = TracerProvider()
# Initialize the Judgeval client and create tracer
client = Judgeval(project_name="default_project")
tracer = client.tracer.create()
# Connect to your existing OTEL infrastructure
tracer_provider.add_span_processor(tracer.get_span_processor())
otel_tracer = tracer_provider.get_tracer(__name__)
# Use native OTEL spans alongside Judgment decorators
def process_request(question: str) -> str:
with otel_tracer.start_as_current_span("process_request_span") as span:
span.set_attribute("input", question)
answer = answer_question(question)
span.set_attribute("output", answer)
return answerResource Attributes
Resource attributes describe the entity producing telemetry data. Common attributes include:
service.name- Name of your serviceservice.version- Version numberdeployment.environment- Environment (production, staging, etc.)service.namespace- Logical grouping
See the OpenTelemetry Resource specification for standard attributes.
Distributed Tracing
Distributed tracing allows you to track requests across multiple services and systems, providing end-to-end visibility into complex workflows. This is essential for understanding how your AI agents interact with external services and how data flows through your distributed architecture.
Sending Trace State
When your agent needs to propagate trace context to downstream services, you can manually extract and send trace context.
uv add judgeval requestspip install judgeval requestsfrom judgeval import Judgeval
from opentelemetry.propagate import inject
import requests
client = Judgeval(project_name="distributed-system")
tracer = client.tracer.create(
resource_attributes={"service.name": "agent-client"}
)
@tracer.observe(span_type="function")
def call_external_service(data):
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": "Bearer ...",
}
inject(headers)
response = requests.post(
"http://localhost:8001/process",
json=data,
headers=headers
)
return response.json()
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = call_external_service({"query": "Hello from client"})
print(result)npm install judgeval @opentelemetry/apiyarn add judgeval @opentelemetry/apipnpm add judgeval @opentelemetry/apibun add judgeval @opentelemetry/apiimport { context, propagation } from "@opentelemetry/api";
import { Judgeval } from "judgeval";
const client = Judgeval.create();
const tracer = await client.nodeTracer.create({
projectName: "distributed-system",
resourceAttributes: { "service.name": "agent-client" },
});
async function makeRequest(url: string, options: RequestInit = {}): Promise<any> {
const headers: Record<string, string> = {};
propagation.inject(context.active(), headers);
const response = await fetch(url, {
...options,
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json", ...headers },
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
}
return response.json();
}
const callExternalService = tracer.observe(async function (data: any) {
return await makeRequest("http://localhost:8001/process", {
method: "POST",
body: JSON.stringify(data),
});
}, "span");
const result = await callExternalService({ message: "Hello!" });
console.log(result);
await tracer.shutdown();Receiving Trace State
When your service receives requests from other services, you can use middleware to automatically extract and set the trace context for all incoming requests.
uv add judgeval fastapi uvicornpip install judgeval fastapi uvicornfrom judgeval import Judgeval
from opentelemetry.propagate import extract
from opentelemetry import context as otel_context
from opentelemetry.instrumentation.fastapi import FastAPIInstrumentor
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
client = Judgeval(project_name="distributed-system")
tracer = client.tracer.create(
resource_attributes={"service.name": "agent-server"}
)
app = FastAPI()
FastAPIInstrumentor.instrument_app(app)
@app.middleware("http")
async def trace_context_middleware(request: Request, call_next):
ctx = extract(dict(request.headers))
token = otel_context.attach(ctx)
try:
response = await call_next(request)
return response
finally:
otel_context.detach(token)
@tracer.observe(span_type="function")
def process_request(data):
return {"message": "Hello from Python server!", "received_data": data}
@app.post("/process")
async def handle_process(request: Request):
result = process_request(await request.json())
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8001)npm install judgeval @opentelemetry/api expressyarn add judgeval @opentelemetry/api expresspnpm add judgeval @opentelemetry/api expressbun add judgeval @opentelemetry/api expressimport express from "express";
import { Judgeval } from "judgeval";
import { context, propagation } from "@opentelemetry/api";
const client = Judgeval.create();
const tracer = await client.nodeTracer.create({
projectName: "distributed-system",
resourceAttributes: { "service.name": "agent-server" },
});
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
app.use((req, res, next) => {
const parentContext = propagation.extract(context.active(), req.headers);
context.with(parentContext, () => {
next();
});
});
const processRequest = tracer.observe(async function (data: any) {
return { message: "Hello from server!", received_data: data };
}, "span");
app.post("/process", async (req, res) => {
const result = await processRequest(req.body);
res.json(result);
});
app.listen(8001, () => console.log("Server running on port 8001"));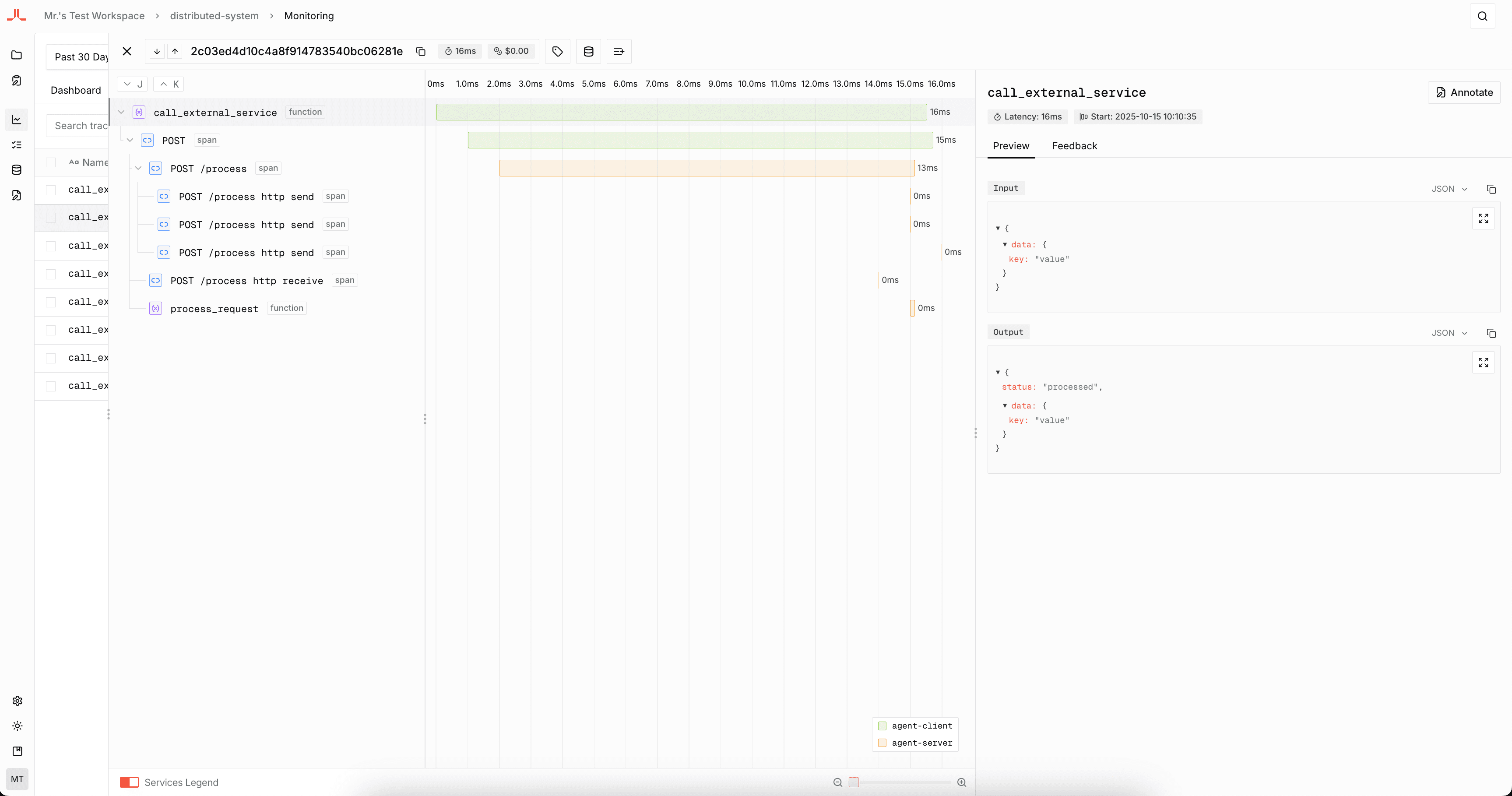

Toggling Monitoring
If your setup requires you to toggle monitoring intermittently, you can disable monitoring by:
- Setting the
JUDGMENT_MONITORINGenvironment variable tofalse(Disables tracing)
export JUDGMENT_MONITORING=false- Setting the
JUDGMENT_EVALUATIONSenvironment variable tofalse(Disables scoring on traces)
export JUDGMENT_EVALUATIONS=falseNext Steps
- Tracer SDK Reference - Explore the complete Tracer API including span access, metadata, and advanced configuration